BACKGROUND
The scope of work concerned a solar power plant located in North America. The objective was to analyze the harmonics produced by the photovoltaic units and measured at the point of common coupling (PCC) in order to verify the compliance with the IEEE 519 standard.
The power plant is composed of 12 Inverters producing 1.2MW each and a substation connecting inverters to the. upstream network.
APPROACH
Model
EMTP® and its capabilities to accurately simulate frequency dependent equipment was used.
For harmonic analysis, an important part of the work is the modelling of the inverters, which are producing harmonics by converting the DC current from photovoltaic cells to AC voltage. The inverters are represented by an equivalent harmonic current source using the harmonics level given by the manufacturer. The fundamental frequency
current and angle are automatically initialized using load-flow results. All harmonic currents align to the fundamental frequency current phase with a relative angle.
The upstream network at the PCC is modelled as a harmonic Thevenin source which is valid for the frequency range of interest. Cables of the collector system are modelled as classic PI models when they are short and wideband model when they are long.
Methodology
Different configurations of the system are studied according to the internal circuits (and the number of inverters) which are connected.
- A frequency scan to measure the system impedance and identify possible resonance frequencies.
- A steady-state analysis simulating the current generated by the power plant and calculating the different harmonic distortion levels (IHD and THD).
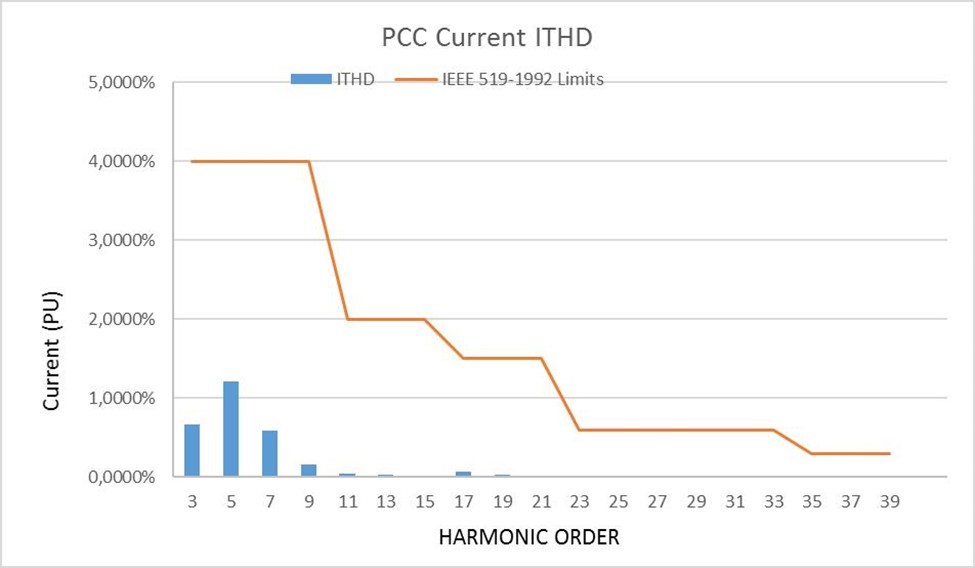
Then, the harmonics levels are compared to the limits given by the IEEE 519 standard.
Find our free course on renewable modeling and simulations.
CONCLUSION
- Current and voltage IHD, voltage THD and current TDD are below the IEEE 519 limits,
- For all configurations of the system, a resonance is identified beyond the range of harmonics of the IEEE 519 standard.
